Product Description
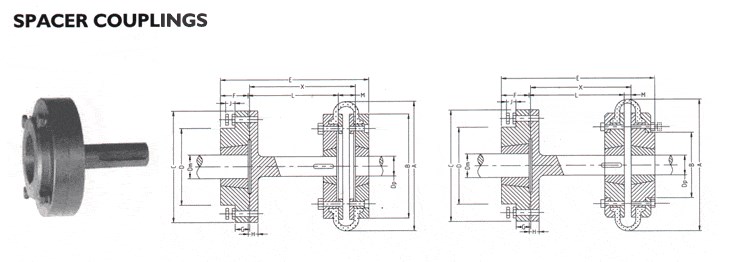
Jaw spacer coupling,
1. The couplings offer a range of hub and element selection to meet different demands.
2. They can absorb shock and cater for incidental misalignment and damp out small amplitude vibrations.
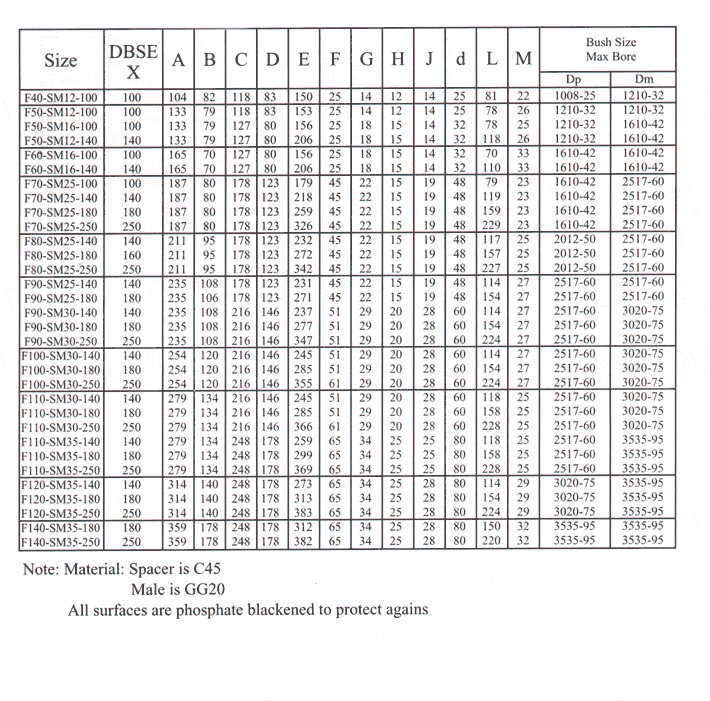
3. NBR, Urethane, Hytrel elements.
4. Compared with Jaw coupling, their flanges are connected by longer shaft ends(DBSE), a spacer kit
consists of a spacer and QF ring kit (wrap+QF ring+3 screws).
5. Customzied requirement is available.
ZheJiang Shine Transmission Machinery Co., Ltd is specialized in manufacturing and selling transmission products.
Our products are exported to the world famous machinery company in Europe, America, South Africa, Australia, Southeast Asia etc.
Our main products include: European pulley, American pulley, Couplings, taper bushing, QD bush, lock element, adjustable motor base, motor rail, sprockets, chain, bolt on hubs, weld on hubs, jaw crusher equipment & spare parts and all kinds of non-standardCasting products etc.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard Or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Shaft Hole: | 0-65mm |
| Torque: | >80N.M |
| Bore Diameter: | 0-65mm |
| Structure: | Flexible |
| Material: | Aluminum/Iron/Rubber |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.00/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How Do Spacer Couplings Compare to Other Types of Couplings in Terms of Performance?
Spacer couplings offer distinct advantages and disadvantages compared to other types of couplings, making them suitable for specific applications:
1. Misalignment Tolerance: Spacer couplings have limited flexibility and can handle only minor misalignment between shafts. In contrast, flexible couplings like elastomeric and gear couplings can accommodate higher levels of misalignment due to their elastic properties.
2. Torque Transmission: Spacer couplings provide excellent torque transmission capabilities, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. They can efficiently transfer torque between shafts without backlash.
3. Maintenance Requirements: Spacer couplings are relatively simple in design and do not require frequent maintenance. They do not have moving parts or wearing elements, reducing the need for regular inspection and replacement.
4. Torsional Stiffness: Spacer couplings offer high torsional stiffness, ensuring precise and reliable torque transmission between the connected equipment.
5. Installation and Alignment: Installing a spacer coupling requires careful alignment between shafts. While it may be more involved compared to some flexible couplings, proper alignment is essential for optimal performance.
6. Cost: Spacer couplings are generally more cost-effective than some high-performance flexible couplings, making them an attractive choice for various industrial applications.
7. Application Suitability: Spacer couplings are commonly used in applications where rigid and reliable torque transmission is required, such as pumps, compressors, and other heavy machinery.
8. Operating Conditions: Spacer couplings can handle high temperatures, making them suitable for applications in challenging environments.
When selecting a coupling for a specific application, it is essential to consider the specific needs of the system, including the required misalignment compensation, torque transmission capacity, maintenance requirements, and operating conditions. Each coupling type has its strengths and limitations, and the choice will depend on the unique demands of the application.

How Does a Spacer Coupling Handle Angular, Parallel, and Axial Misalignment?
A spacer coupling is a type of flexible coupling that is designed to accommodate different types of misalignment between shafts. Here’s how it handles angular, parallel, and axial misalignment:
1. Angular Misalignment: Angular misalignment occurs when the axes of the two shafts are not parallel but intersect at a certain angle. A spacer coupling can handle angular misalignment by allowing the flexible element (such as an elastomeric or metallic component) to flex and bend when the shafts are not perfectly aligned. This bending action allows the coupling to compensate for the angular displacement between the shafts and transmit torque smoothly.
2. Parallel Misalignment: Parallel misalignment occurs when the axes of the two shafts are parallel but are offset laterally. A spacer coupling can handle parallel misalignment by virtue of its design. The spacer element (a cylindrical piece that connects the two coupling halves) provides the required lateral space between the shafts. This space allows the shafts to have a slight offset without inducing excessive stress on the machinery, thereby minimizing the risk of premature wear or failure.
3. Axial Misalignment: Axial misalignment occurs when the two shafts move closer together or farther apart along their axis. Some spacer couplings may have limited axial movement capabilities, which can help accommodate slight axial misalignment. However, it’s essential to ensure that the axial displacement is within the coupling’s specified limits to avoid overloading the coupling or the connected equipment.
Overall, spacer couplings are designed to be flexible and provide some degree of misalignment accommodation, but their ability to handle misalignment depends on their specific design and material properties. It’s essential to select the appropriate type and size of spacer coupling based on the expected misalignment and operational requirements of the machinery to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the coupling and the connected components.


editor by CX 2024-03-27